If you’ve ever felt overwhelmed trying to choose the right CRM, you’re not alone.
The market is crowded with options that all promise to streamline your sales, but when every platform claims to be “the best CRM tool,” how do you actually know which one fits your business?
Choosing CRM is a strategic decision. In this guide, we’ll walk you through a clear, practical process for choosing a CRM that fits your team’s goals, workflows, and growth stage.
Whether you’re buying your first CRM or replacing one that never quite worked out, these steps will help you make a confident, informed choice.
Step 1: Clarify Your Sales Team’s Core Needs
The first and most crucial step in choosing CRM is understanding your sales team’s core needs.
A CRM is only as effective as the way it supports your team’s workflow, so before evaluating features or pricing, you need a clear picture of what your team requires to sell efficiently.
Assess Current Pain Points
Start by looking at the challenges your sales team faces.
Are leads slipping through the cracks? Is follow-up inconsistent? Or maybe reporting is cumbersome and time-consuming? Documenting these pain points will help you identify the areas where a CRM can provide the most value.
Identify Key Sales Processes
Next, map out your sales processes from lead generation to closing deals. Consider questions like:
- How are leads currently captured and qualified?
- What steps do sales reps follow to move prospects through the pipeline?
- How is success measured at each stage?
Understanding these processes allows you to choose a CRM that aligns with your team’s workflow rather than forcing your team to adapt to the software.
Define Must-Have Features
Once pain points and processes are clear, list the features your team truly needs. This may include contact and lead management, pipeline tracking, task automation, or reporting and analytics.
Prioritizing features helps you avoid investing in complex tools your team may never use.
Gather Team Input
Your sales team’s insight is invaluable. Conduct interviews or surveys to understand what tools they wish they had and which current tools frustrate them.
Involving the team in this early stage ensures higher adoption rates later on and prevents overlooking critical needs.
Step 2: Set Evaluation Criteria That Match Your Business Goals
After clarifying your sales team’s core needs, the next step in choosing CRM is setting evaluation criteria that align with your business goals.
This ensures that when you compare CRM options, you focus on what truly matters for your organization’s growth, efficiency, and long-term success.
Align CRM Features With Business Objectives
Start by connecting your CRM evaluation criteria to your business goals. If your goal is to increase sales efficiency, prioritize features like automated workflows, task reminders, and lead scoring.
By aligning your CRM criteria with strategic objectives, you’ll avoid investing in systems that look impressive but don’t drive results.
Consider Usability and Adoption
A CRM can be powerful, but it’s useless if your team doesn’t use it consistently. Usability should be a top criterion in your evaluation process. Look for platforms with intuitive navigation, easy data entry, and minimal learning curves.
A user-friendly interface encourages adoption and reduces the need for extensive training, making choosing CRM not just about features, but about how seamlessly your team can integrate it into daily workflows.
Evaluate Key Features
When evaluating CRM options, consider the features your team identified in Step One. Core capabilities to assess may include:
- Pipeline management: Visualize and manage deals efficiently.
- Automation: Reduce repetitive tasks and follow-ups.
- Contact management: Keep detailed customer records organized.
- Reporting and analytics: Track performance against KPIs.
- Integrations: Connect with email, marketing, and other business tools.
Think About Scalability
Your business is growing, and your CRM should grow with it. Evaluate whether each CRM can accommodate an increasing number of users, handle expanding data, and adapt to more complex processes.
Scalability ensures that the system you choose today remains effective as your team and business evolve.
Assess Mobile Accessibility and Customization
Modern sales teams work on the go. A mobile-accessible CRM allows reps to update deals, check tasks, and access customer information anywhere, anytime.
Additionally, customization options such as role-based dashboards, custom fields, and workflows let your CRM fit your unique processes rather than forcing you to adapt to a rigid structure.
Step 3: Prioritize Features That Matter Most
The next step in choosing CRM is understanding which features truly matter.
Not all CRMs are created equal, and identifying the must-have, nice-to-have, and potentially problematic features will help you make a smart, practical choice.
Must-Have CRM Features for Sales Teams
For any sales team, certain core features are non-negotiable:
- Contact and lead management: Centralized storage of customer information ensures no lead falls through the cracks.
- Pipeline and deal tracking: Visual pipelines let reps see where each deal stands and what actions are needed to close it.
- Task automation: Automatic reminders, follow-ups, and task assignments save time and reduce human error.
- Account-based management: Organize and track activities by company, not just individual contacts.
- Complex workflow support: Handle multi-step approval processes and deal hierarchies efficiently.
- Custom fields and pipelines: Tailor the CRM to match your industry-specific sales cycles.
- Reporting and analytics: Real-time insights into performance metrics help managers make data-driven decisions.
- Integration capabilities: Seamless connection with email, calendars, and marketing tools keeps all processes unified.
Advanced Features to Watch
Once the basics are covered, some CRMs offer advanced features that can give teams a competitive edge:
- Predictive analytics: Uses historical data to forecast deals and highlight high-potential leads.
- AI scoring and lead prioritization: Helps reps focus on leads most likely to convert.
- Sales automation beyond the basics: Advanced workflows that trigger multi-step campaigns automatically.
While these advanced features can be powerful, they are most beneficial when your team is ready to leverage them fully. Otherwise, they may complicate adoption without delivering real ROI.
Red Flags: Features That Can Backfire
Not every shiny feature is worth it. Watch out for potential pitfalls:
- Over-complexity: CRMs with too many options or convoluted workflows can frustrate users and slow adoption.
- Unnecessary add-ons or modules: Extras you don’t need often drive up cost and clutter the system.
- Rigid workflows: Systems that cannot be customized to your sales process can create friction instead of solving problems.
Step 4: Compare CRM Tools Based on Real Use Cases
Evaluating CRMs in the context of how your team will actually use them provides insight that feature lists and demos alone cannot offer.
Simulate Your Sales Processes
Start by testing how each CRM handles your specific sales workflows. For example:
- Can you easily track a lead from first contact through to deal closure?
- How simple is it to assign tasks, update deal stages, or set reminders?
- Does the system handle multi-step approval processes for complex B2B deals?
By mapping real use cases onto each CRM, you can see which platforms support your team’s daily activities and which might create friction.
Step 5: Test for Usability and User Adoption
The next critical step in choosing CRM is testing for usability and user adoption. Even the most feature-rich CRM is only valuable if your sales team can use it effectively.
Conduct Hands-On Demos
Begin with product demos, ideally guided by a sales representative from the CRM provider. These demos allow your team to explore the interface, try core features, and see how the CRM functions in a controlled environment.
Pay attention to:
- How easy it is to navigate the system.
- How quickly data can be entered or retrieved.
- Whether workflows match your team’s existing processes.
Involve Your Team in Testing
User adoption is directly tied to your team’s comfort and confidence with the platform. Invite a small group of sales reps to test the CRM over a trial period.
Ask them to perform daily tasks such as updating deals, creating tasks, sending emails, and generating reports. Collect feedback on:
- Ease of use
- Speed of completing tasks
- Clarity of dashboards and notifications
- Any obstacles or frustrations encountered
Identify Adoption Barriers
Look out for features or workflows that could hinder adoption, such as:
- Overly complex navigation
- Mandatory steps that slow down tasks
- Unnecessary features that clutter the interface
Step 6: Evaluate Integration Capabilities
A CRM does not operate in isolation. Your sales team relies on a stack of tools, and the CRM you choose must seamlessly connect with these systems to streamline workflows and maximize efficiency.
Assess Compatibility with Your Existing Sales Stack
Start by identifying the tools your team already uses, such as email platforms, marketing automation systems, customer support software, and analytics tools.
A CRM that integrates with these systems can centralize data, eliminate duplicate entries, and ensure your sales reps have a complete view of each customer interaction.
Review API and CRM Integration Options
Most modern CRMs offer APIs or built-in integrations to connect with third-party tools. Evaluate:
- The ease of setting up integrations
- Available native integrations versus custom API connections
- Whether the integrations cover the specific workflows your team uses
CRMs with flexible APIs allow your IT or operations teams to customize connections, automate data flows, and adapt the CRM as your tech stack evolves.
Consider Workflow Automation Across Tools
Integration isn’t just about connecting systems—it’s about enabling smooth workflows. For example:
- Automatically syncing leads from your website or marketing software into the CRM
- Triggering sales follow-up tasks or notifications when a customer interacts with your email campaigns
- Pushing CRM data to reporting dashboards or analytics platforms
Step 7: Assess CRM Implementation and Support Resources
Even the best CRM can fall short if the setup is overly complicated or your team doesn’t have access to adequate training and ongoing assistance.
Evaluate Implementation Time and Complexity
Start by estimating how long it will take to set up the CRM and get your team fully operational. Consider factors such as:
- Data migration from existing systems
- Customization of pipelines, dashboards, and fields
- Setting up user roles and permissions
CRMs vary widely in implementation complexity. Choosing a platform with a manageable setup process can reduce downtime and help your team start benefiting from the system sooner.
Review Training Options
Effective adoption relies on proper training. Evaluate what training resources the vendor provides, such as:
- Live onboarding sessions
- Video tutorials and webinars
- Step-by-step guides and knowledge bases
A CRM with comprehensive training options accelerates learning, reduces errors, and ensures your team uses the platform effectively from day one.
Check Availability of Ongoing Support
Your team will inevitably encounter questions or issues after launch. Assess the vendor’s ongoing support resources:
- Customer support channels (chat, email, phone) and responsiveness
- Access to dedicated account managers or success specialists
- Community forums or user groups for peer support
Reliable support ensures your team can resolve issues quickly and maintain productivity without unnecessary frustration.
Consider Long-Term Maintenance
Implementation and support also include the long-term perspective.
Determine if updates, system enhancements, and troubleshooting are straightforward and whether the vendor proactively communicates improvements or changes.
Step 8: Check Data Security and Compliance Standards
Your CRM will house sensitive customer information, and ensuring it is protected is essential for maintaining trust, avoiding legal risks, and supporting long-term business growth.
Evaluate Data Protection Measures
Start by examining how each CRM safeguards customer data. Key factors to consider include:
- Encryption: Data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest
- Access control: Ensure the system allows role-based permissions so users can only access information relevant to their role.
- Backup and recovery: Check how the CRM handles regular backups and whether data can be restored quickly in case of loss.
These measures prevent unauthorized access, minimize the risk of breaches, and ensure data integrity.
Review Audit Logs and Monitoring
Audit logs provide a detailed record of who accessed data, when, and what changes were made.
A CRM with robust audit trails enhances accountability and helps your team quickly detect any unusual or unauthorized activity.
Monitoring features can alert administrators to potential security risks in real time.
Verify Compliance and Certifications
Depending on your industry and customer base, compliance with data protection regulations is critical. Ask whether the CRM adheres to relevant standards such as:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) for handling EU customer data
- HIPAA if you work with healthcare-related information
- SOC 2 or ISO 27001 certifications for general data security and operational practices
Step 9: Consider Budget and ROI Potential
Selecting a CRM is not just about cost; it’s about maximizing the value you get for your investment while ensuring long-term efficiency and growth.
Calculate Total Cost of Ownership
Start by considering the total cost of ownership (TCO), which goes beyond the subscription fee. Include:
- Implementation costs: Data migration, customization, and setup expenses
- Training costs: Time and resources needed to onboard your sales team
- Maintenance and support fees: Ongoing support, updates, and potential add-ons
Accounting for all costs ensures you have a realistic view of what the CRM will actually cost your business over time.
Compare Value Over Price
While it’s tempting to choose the cheapest option, value should drive your decision. Evaluate how the CRM supports your team’s productivity, improves sales efficiency, and enhances reporting and analytics.
A slightly higher-priced CRM that reduces manual work, boosts deal closure rates, and integrates seamlessly with your stack often provides a higher ROI than a lower-cost system with limited capabilities.
Factor in Scalability Costs
As your business grows, your CRM needs may evolve. Ensure the platform can scale without exponentially increasing costs.
Some systems charge per user or require costly upgrades for advanced features, so factoring in scalability now prevents surprises later.
Step 10: Shortlist and Conduct Final Vendor Comparison
The final step in choosing CRM is shortlisting top candidates and conducting a thorough comparison to make a confident decision.
This step ensures you select a CRM that fits your team’s workflow, budget, and long-term goals.
Build a CRM Scorecard
A scorecard is a structured way to evaluate multiple CRM vendors objectively. List the key criteria from your previous steps—usability, integrations, features, security, implementation, support, and ROI potential—and assign scores to each CRM.
Weight criteria according to importance for your business. This visual comparison helps highlight which CRM best meets your needs.
Here’s a sample CRM scorecard:
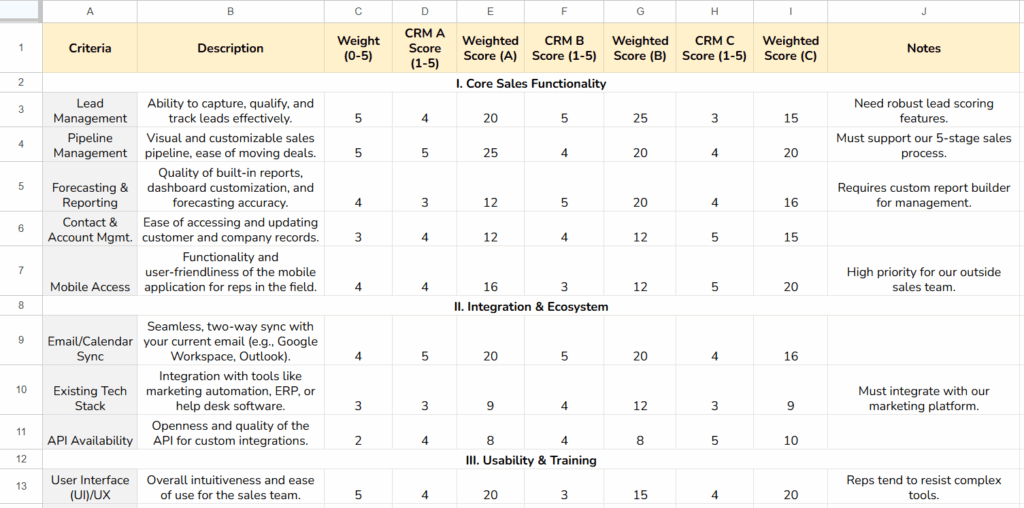
Tips for Choosing Between Finalists
- Compare strengths and weaknesses: Look beyond feature lists and focus on how each CRM performs in real-world scenarios.
- Consider team feedback: Your sales reps’ opinions during testing are crucial—high adoption often outweighs small feature differences.
- Review total cost of ownership: Factor in all implementation, training, and subscription costs.
- Check vendor reputation: Look at reviews, case studies, and customer references to ensure reliability.
Bonus: CRM Buyer Mistakes to Avoid
Even after carefully following all the steps in choosing CRM, some businesses still end up with a platform that doesn’t deliver the results they expected.
Here are the most frequent CRM buyer mistakes and how to steer clear of them.
Buying for Features You’ll Never Use
It’s easy to be impressed by a CRM’s long list of features. But more doesn’t always mean better.
Many companies invest in complex platforms packed with advanced capabilities they never touch. This leads to wasted budget, longer setup times, and frustrated users.
Avoid it: Focus on features that directly support your sales processes and business goals. A simpler, more targeted CRM that your team actually uses will always outperform an overcomplicated one.
Failing to Involve Your Sales Team
Your sales reps are the people who’ll use the CRM daily so their input is invaluable. Choosing a system without their feedback often leads to low adoption and resistance to change.
Avoid it: Involve your sales team early. Ask for their input on pain points, workflows, and must-have features. Testing CRM demos with real users ensures buy-in and smooth adoption.
Bottom Line
Choosing CRM isn’t about finding the “best” software on the market; it’s about finding the right one for your business. A thoughtful selection process saves time, eliminates guesswork, and turns your CRM from a data-entry chore into a growth engine.
Approach your CRM decision like a strategic investment, not a quick purchase. When you choose intentionally, you build the foundation for stronger customer relationships, smarter sales decisions, and long-term success.










